A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a type of injury that occurs when a blow or jolt to the head causes damage to the brain. TBIs can range from mild to severe and can cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on the extent and location of the damage.
Treatment for traumatic brain injuries will vary depending on the severity of the injury but may include rest, medication, rehabilitation, and surgery in more severe cases. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you or someone you know has suffered a traumatic brain injury.
What Causes TBI?
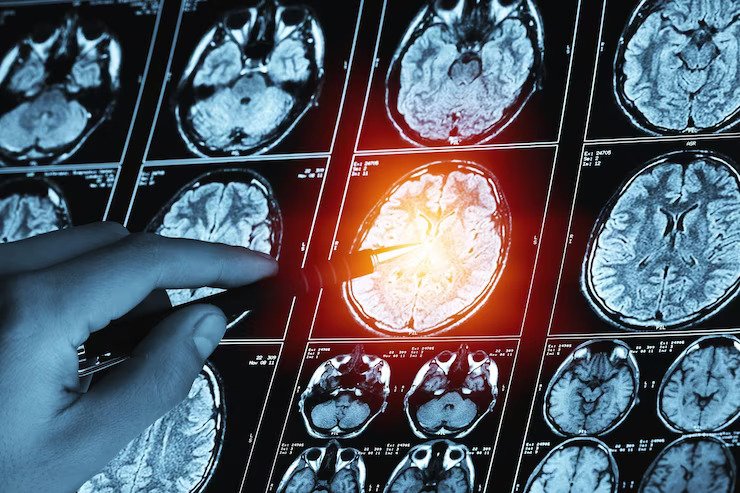
There are many possible causes of traumatic brain injury (TBI), including:
- Falls are the most common cause of TBI, particularly in children and older adults.
- Motor vehicle accidents: Car, motorcycle, and bicycle accidents are common causes of TBI.
- Sports injuries: High-impact sports such as football, hockey, and boxing can result in TBI.
- Physical violence: Assaults, domestic violence, and child abuse can result in TBI.
- Explosive blasts and other combat injuries: Military personnel are at high risk of TBI due to exposure to explosions and other combat-related injuries.
- Workplace injuries: TBI can occur in workplaces with a risk of falling objects or head injuries from machinery.
- Medical conditions: Certain conditions, such as strokes or brain tumors, can also cause TBI.
It is important to note that not all blows or jolts to the head result in TBI, and the severity of TBI can vary widely.
However, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect that you or someone you know has suffered a traumatic brain injury, as prompt diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes.
Symptoms Of TBI
Symptoms of traumatic brain injury (TBI) can vary depending on the severity and location of the injury.
Some common symptoms of TBI include:
- Physical Symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, nausea or vomiting, sensitivity to light or sound, fatigue, and sleep disturbances.
- Cognitive Symptoms: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, confusion, and difficulty with reasoning or problem-solving.
- Emotional Symptoms: Depression, anxiety, mood swings, irritability, and impulsivity.
- Behavioral Symptoms: Agitation, aggression, and changes in social behavior or personality.
- Sensory Symptoms: Blurred vision, ringing in the ears, a bad taste in the mouth, and changes in the ability to smell.
In severe cases of TBI, the individual may experience loss of consciousness, seizures, or coma. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know experiences these symptoms after a head injury. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes for TBI.
TBI is a medical condition that makes patients eligible for TBI Settlements and Disability Benefits. Visit the site to see the requirement for eligibility.
How To Determine The Severity Of TBI?
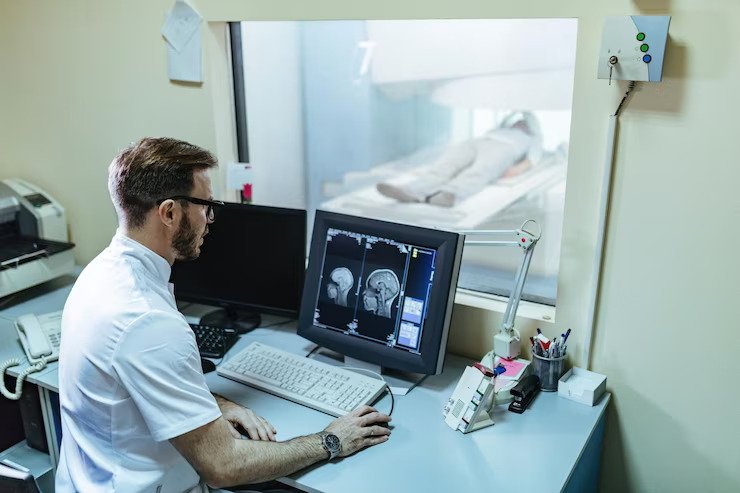
The severity of traumatic brain injury (TBI) is determined by several factors, including the initial Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, duration of unconsciousness or amnesia, imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and clinical assessments of cognitive, physical, and behavioral function.
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a tool used to assess the level of consciousness. It measures eye opening, verbal response, and motor response, and scores based on the activity.
Other factors used to determine TBI severity include the duration of unconsciousness or amnesia, defined as the length of time the person was unable to recall events before or after the injury, as well as imaging studies such as CT or MRI scans that can detect brain abnormalities.
Clinical assessments of cognitive, physical, and behavioral function are also used to determine the severity of TBI. These may include memory, attention, problem-solving, and motor function tests, as well as assessments of mood, behavior, and social function.
Determining the severity of TBI is important for developing a treatment plan and predicting outcomes. Treatment for TBI may include rest, medication, rehabilitation, and surgery in more severe cases. The goal of treatment is to minimize the effects of the injury and maximize the individual’s ability to function in daily life.
How Is TBI Measured?
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is typically measured using a combination of objective and subjective measures.
Here are some common methods used to measure TBI:
- Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): The GCS is a tool used to assess the level of consciousness in a person following a head injury. It measures eye opening, verbal response, and motor response, and scores range from 3 (indicating a severe TBI) to 15 (indicating a mild TBI).
- Imaging studies: Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect brain abnormalities and are often used to diagnose and monitor TBI.
- Clinical assessments: Clinical assessments of cognitive, physical, and behavioral function are used to determine the severity of TBI. These may include memory, attention, problem-solving, and motor function tests, as well as assessments of mood, behavior, and social function.
- Symptom checklists: Symptom checklists may assess the individual’s subjective experience of TBI symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, or cognitive difficulties.
- Functional assessments: Functional assessments measure the individual’s ability to perform daily activities such as dressing, grooming, and cooking. These assessments determine the level of functional impairment and the need for rehabilitation.
Determining the severity of TBI is important for developing a treatment plan and predicting outcomes. Treatment for TBI may include rest, medication, rehabilitation, and surgery in more severe cases. The goal of treatment is to minimize the effects of the injury and maximize the individual’s ability to function in daily life.
Can TBI Fully Recover?
The recovery from traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies depending on the injury’s severity, the damage’s location, the age and overall health of the individual, and the quality of care received.
In some cases, TBI can fully recover, while individuals may experience lasting effects in others.
Mild TBI typically resolves within a few weeks to months with appropriate care, including rest and avoiding activities that could worsen symptoms. Most people who experience mild TBI recover fully and return to their pre-injury level of functioning.
Moderate to severe TBI, on the other hand, can result in long-term or permanent physical, cognitive, and behavioral impairments.
However, with proper rehabilitation and ongoing treatment, individuals with moderate to severe TBI can significantly improve their function and quality of life. The extent of recovery varies widely among individuals and depends on many factors.
Note that TBI recovery is a gradual process that can take several months or even years to recover fully. It’s also important to seek prompt medical attention following a head injury to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment, which can improve outcomes for TBI.
Affect Of TBI On Patient’s Life
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) can significantly impact a patient’s life, depending on the severity of the injury.
Here are some of the ways TBI can affect a patient’s life:
- Physical effects: TBI can cause physical effects such as headaches, dizziness, fatigue, vision and hearing problems, and seizures.
- Cognitive effects: TBI can also affect cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and executive functioning.
- Emotional and behavioral effects: TBI can cause emotional and behavioral changes such as irritability, depression, anxiety, aggression, and impulsivity.
- Social effects: TBI can impact social functioning, making it difficult for patients to maintain relationships, work, and participate in social activities.
- Financial effects: TBI can be expensive, with costs including medical bills, rehabilitation, and lost wages due to the inability to work.
These effects can be short-term or long-lasting, depending on the severity of the injury and the quality of care received.
Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation, can help individuals with TBI improve their function and quality of life.
Read Also: